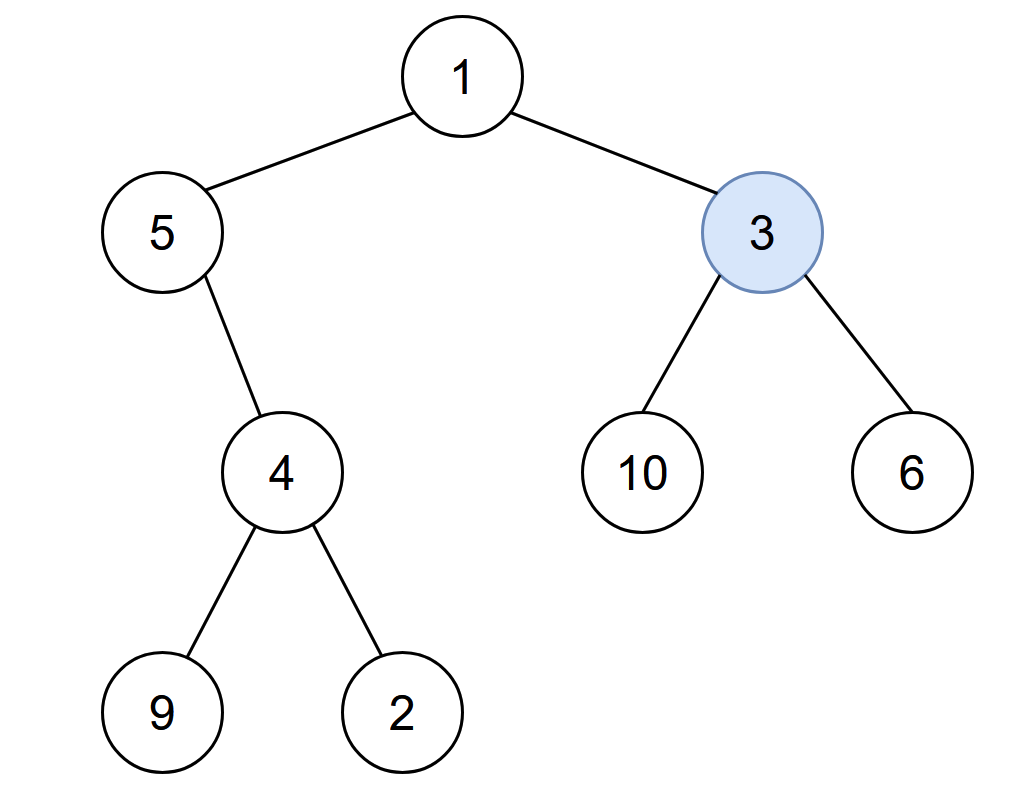
You are given the root of a binary tree with unique values, and an integer start. At minute 0, an infection starts from the node with value start.
Each minute, a node becomes infected if:
Return the number of minutes needed for the entire tree to be infected.
Example 1:

Input: root = [1,5,3,null,4,10,6,9,2], start = 3
Output: 4
Explanation: The following nodes are infected during:
- Minute 0: Node 3
- Minute 1: Nodes 1, 10 and 6
- Minute 2: Node 5
- Minute 3: Node 4
- Minute 4: Nodes 9 and 2
It takes 4 minutes for the whole tree to be infected so we return 4.
Example 2:

Input: root = [1], start = 1
Output: 0
Explanation: At minute 0, the only node in the tree is infected so we return 0.
Constraints:
[1, 105].1 <= Node.val <= 105start exists in the tree.Looking at the problem, it was evident to use Breadth-First Search (BFS) to find the distance of the farthest leaf from the start. Therefore, one approach is to simply convert the tree into a graph with adjacency dictionary adj. And then simply apply BFS over the new graph from the start as the source node and find out the distance of the farthest leaf. This will be the time required for the binary tree to be infected.